
If the value of the calculated F-statistic is more than the F-critical value (for a specific α/significance level), then we reject the null hypothesis. The F-statistic calculated here is compared with the F-critical value for making a conclusion. In that case, we cannot reject the null hypothesis. It’s calculated by dividing MS B and MS W. Lower the F-Ratio, more similar are the sample means. If the variance caused by the interaction between the samples is much larger when compared to the variance that appears within each group, then it is because the means aren’t the same.į test statistic: It measures if the means of different samples are significantly different or not. The whole idea behind the analysis of variance is to compare the ratio of between-group variance to within-group variance. Total Variation: It is the sum of the squares of the differences of each mean with the grand mean which is also the sum of SS B and SS W. Mean sum of Square for within-group variability (MS W): It’s calculated by dividing the Sum of Square (within-group variability) and the degrees of freedom (the sum of the individual degrees of freedom for each sample). Since each sample has degrees of freedom equal to one less than their sample sizes, and there are k samples, the total degrees of freedom is k less than the total sample size: df = N – k.Sum of Square for within-group variability (SS W): It is the aggregate of squared deviation of each value from its respective sample mean.Each sample is considered independently, no interaction between samples is involved and the variability between the individual points in the sample is calculated. Within-Group Variability (Mean Square Effect): It refers to variations caused by differences within individual groups as not all the values within each group are the same. Mean sum of Square for between-group variability (MS B): It’s calculated by dividing the Sum of Square (between-group variability) and the degrees of freedom (number of sample means – 1).
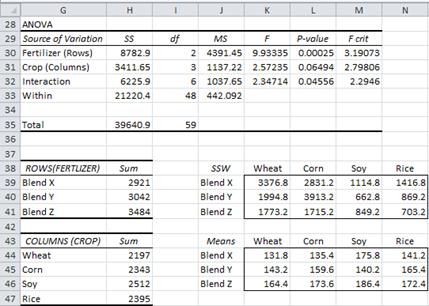
Sum of Square for between-group variability (SS B): It’s the aggregate of squared differences between the sample mean and the grand mean.To calculate the Mean Square effect, we look at each sample to calculate the difference between its mean and the grand mean. Note that we still can’t tell which group is specifically different from rest of the others.īetween-Group Variability (Mean Square Effect): It refers to variations between the distributions of individual groups as the values within each group are different. Alternate hypothesis – At least one of the sample means is different from the rest of the sample means.Null hypothesis – All sample means are equal, or they don’t have any significant difference.In the case of ANOVA, we have a Null Hypothesis and an Alternate Hypothesis.

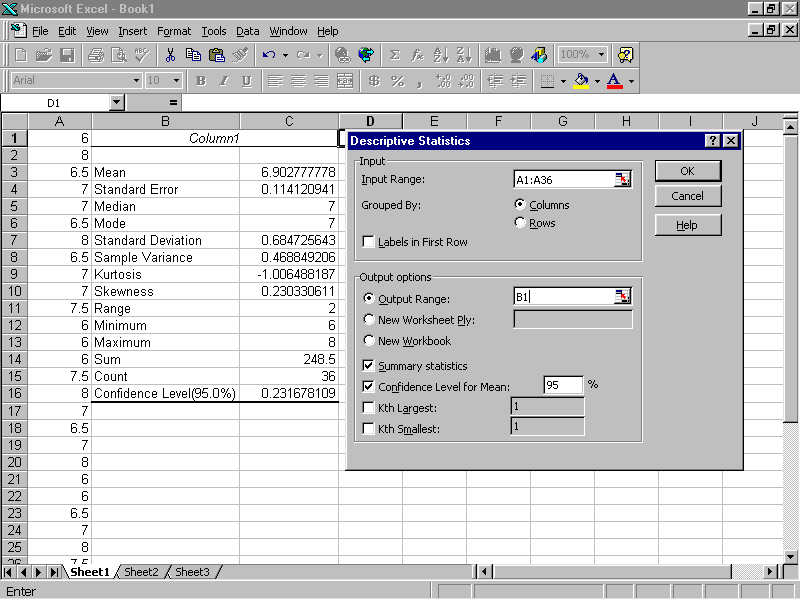
Hypothesis: A hypothesis is a statement which is suggested as a possible explanation for a particular situation or condition, but which has not yet been proved to be correct.

In ANOVA, we use two types of means – the grand mean (mean of the entire sample) and group sample means (mean of each individual groups). Grand Mean: Mean is a simple or arithmetic average of a range of values.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
